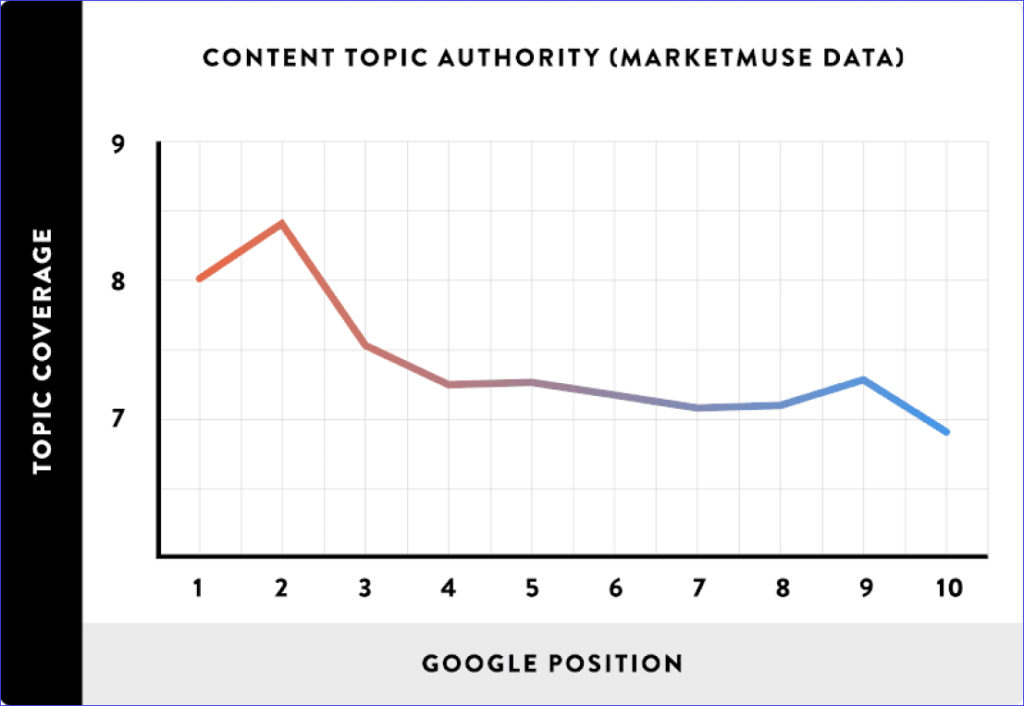
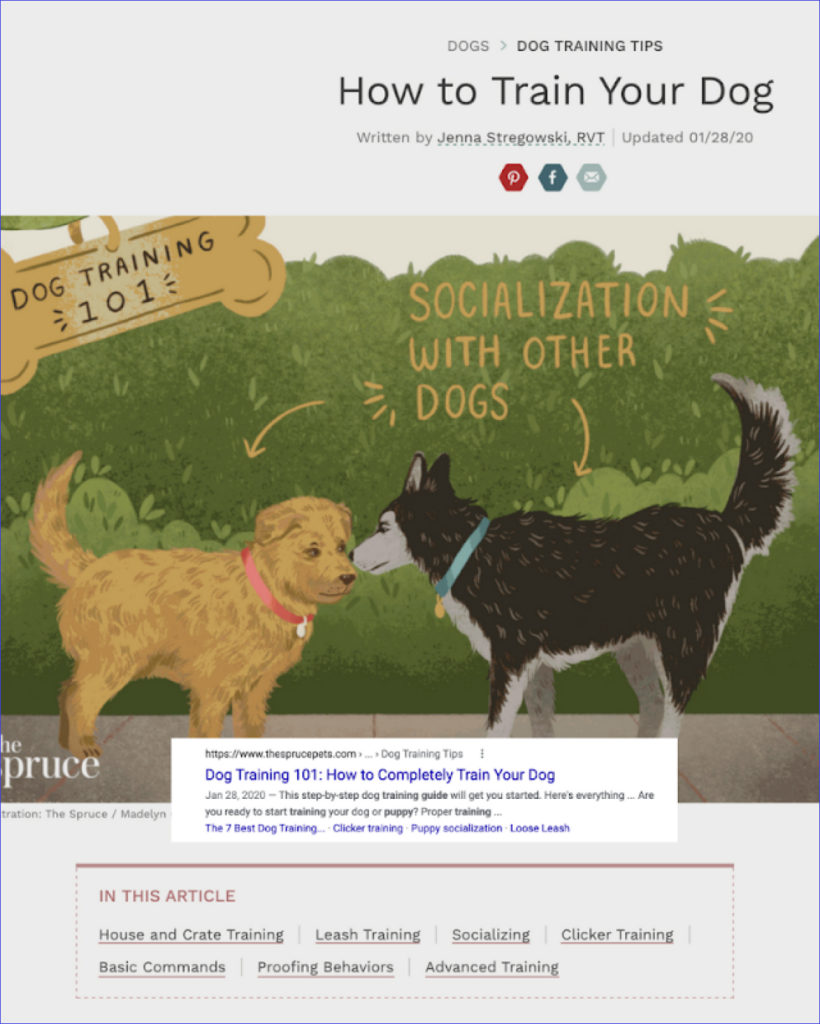
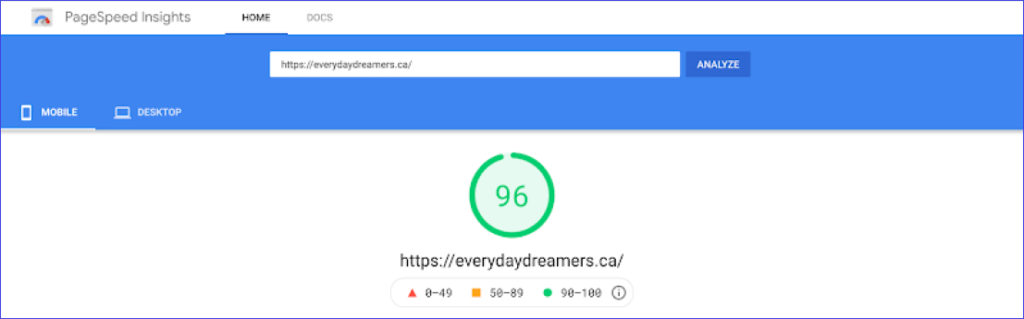
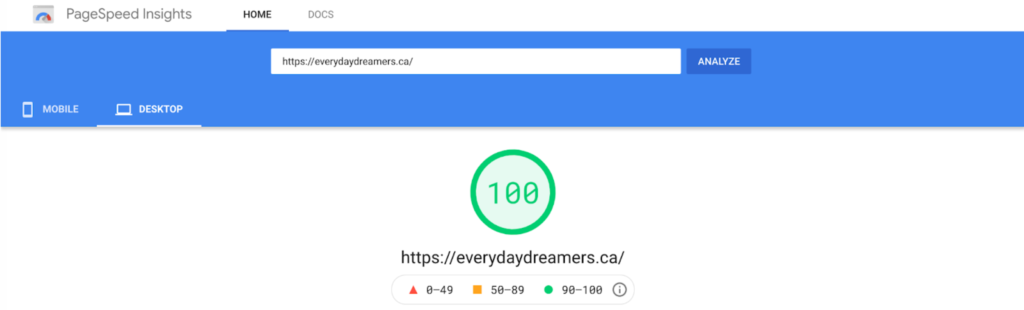
What You Need To Know About Google’s Ranking Algorithm
You wouldn’t drive a car without taking Driver’s Ed. And you wouldn’t participate in an Ironman Triathlon without extensive training. The same goes for website optimization — yet many people do it without learning how Google’s ranking algorithm works.
Sure, you can learn to drive without formal lessons. And you can finish an Ironman. But you’re going to have a harder time and won’t get the same results as someone who prepared themselves.
So before you optimize another website, take some time to understand how Google’s ranking algorithm works. It’ll make your life — and your job — much easier.